Auto Insurance: Coverage, Costs, Rules, and How to Choose the Right Policy
Auto insurance is something almost every driver needs, yet many people buy a policy without fully understanding how it works. Whether you drive daily or only occasionally, auto insurance plays a vital role in protecting your finances when accidents, theft, or unexpected damage occur.
In this guide, we’ll break down auto insurance in plain language. You’ll learn what is auto insurance, why it’s required, the types of coverage available, how costs are calculated, and how to choose the right policy for your needs, without confusion or technical terms.
What Is Auto Insurance?
Auto insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company. You agree to pay a regular fee called a premium, and in return, the insurer agrees to help cover financial losses related to accidents, theft, or vehicle damage, as defined in your policy.
If you cause an accident, auto insurance can pay for:
- Damage to other people’s vehicles or property
- Medical bills for injured parties
- Legal costs if you are sued
Depending on the coverage you choose, it can also help pay for repairs to your own car or replace it if it’s stolen or totaled.
Why Auto Insurance Is Important
Driving always involves risk. Even careful drivers can face accidents caused by weather, road conditions, or other drivers. Auto insurance protects you from paying large, unexpected bills out of pocket.
Here’s why auto insurance matters:
1. It Protects Your Finances
Vehicle repairs and medical expenses can be extremely costly. Auto insurance helps reduce the financial burden.
2. It’s Required by Law in Most Places
In the U.S., auto insurance is mandatory in every state except New Hampshire. In India, third-party insurance is required under the Motor Vehicles Act.
3. It Protects Other People
If you cause an accident, insurance helps cover injuries or damage suffered by others.
4. It Gives Peace of Mind
Knowing you’re covered allows you to drive without constant worry about worst-case scenarios.
Is Auto Insurance Mandatory?
In the United States
Most U.S. states and Washington, D.C. require drivers to carry minimum auto insurance coverage. These laws vary by state, but nearly all require:
- Bodily injury liability
- Property damage liability
If you finance or lease a car, lenders often require additional coverage like collision and comprehensive insurance.
In India
Auto insurance is mandatory, and at minimum, drivers must carry third-party liability insurance. This covers injury, death, or property damage caused to others.
Failing to meet legal insurance requirements can lead to:
- Fines
- License suspension
- Vehicle registration issues
- Legal penalties for repeat offenses
How Auto Insurance Works
Auto insurance works by transferring financial risk from you to the insurer.
- You choose coverage types and limits
- You pay a premium (monthly, quarterly, or yearly)
- If a covered event occurs, you file a claim
- You pay your deductible (if applicable)
- The insurer pays the remaining covered costs
Policies are usually issued for six months or one year and must be renewed to stay active.
Who Is Covered Under an Auto Insurance Policy?
A standard personal auto insurance policy usually covers:
- You, the policyholder
- Family members listed on the policy
- Someone driving your car with your permission
Your policy also generally covers you when driving someone else’s car, as long as it’s for personal use and you have permission.
What Is Not Covered?
- Commercial use (delivery driving, business transport)
- Ride-sharing services like Uber or Lyft (unless you have extra coverage)
Some insurers offer add-on coverage for ride-share drivers at an additional cost.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage Explained
Auto insurance policies are made up of different coverage types. You can choose only what’s legally required or add extra protection based on your needs.
1. Liability Coverage
Liability coverage pays for damage or injuries you cause to others.
Bodily Injury Liability
Covers medical expenses, lost income, and legal costs if someone is injured or killed in an accident you cause.
Property Damage Liability
Pays for damage to another person’s vehicle or property, such as fences, buildings, or utility poles.
2. Medical Coverage
Medical Payments (MedPay)
Covers medical and funeral expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who caused the accident.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Also known as no-fault insurance, PIP covers:
- Medical bills
- Lost wages
- Rehabilitation costs
- Funeral expenses
PIP is required in some states and optional in others.
3. Uninsured and Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured Motorist Coverage
Protects you if you’re hit by a driver who has no insurance.
Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Helps cover costs when the at-fault driver’s insurance isn’t enough to pay for all damages.
These coverages are highly recommended, even when optional.
4. Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for damage to your own car caused by:
- A crash with another vehicle
- Hitting an object like a tree, pole, or guardrail
- Pothole damage or rollovers
It applies regardless of who caused the accident.
5. Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects your car from non-collision events such as:
- Theft
- Fire
- Floods or hail
- Vandalism
- Falling objects
- Animal collisions
Many comprehensive policies also cover windshield repairs.
6. Glass Coverage
Glass coverage provides extra protection for:
- Windshields
- Side and rear windows
- Sunroofs
In some states, windshield repairs have no deductible.
7. Gap Insurance
Cars lose value quickly. If your car is totaled or stolen, insurance only pays its current market value, not what you still owe.
Gap insurance covers the difference between:
- What you owe on your loan or lease
- What your car is worth
Gap coverage is often included in leases and is usually cheaper when added to your auto policy rather than purchased separately.
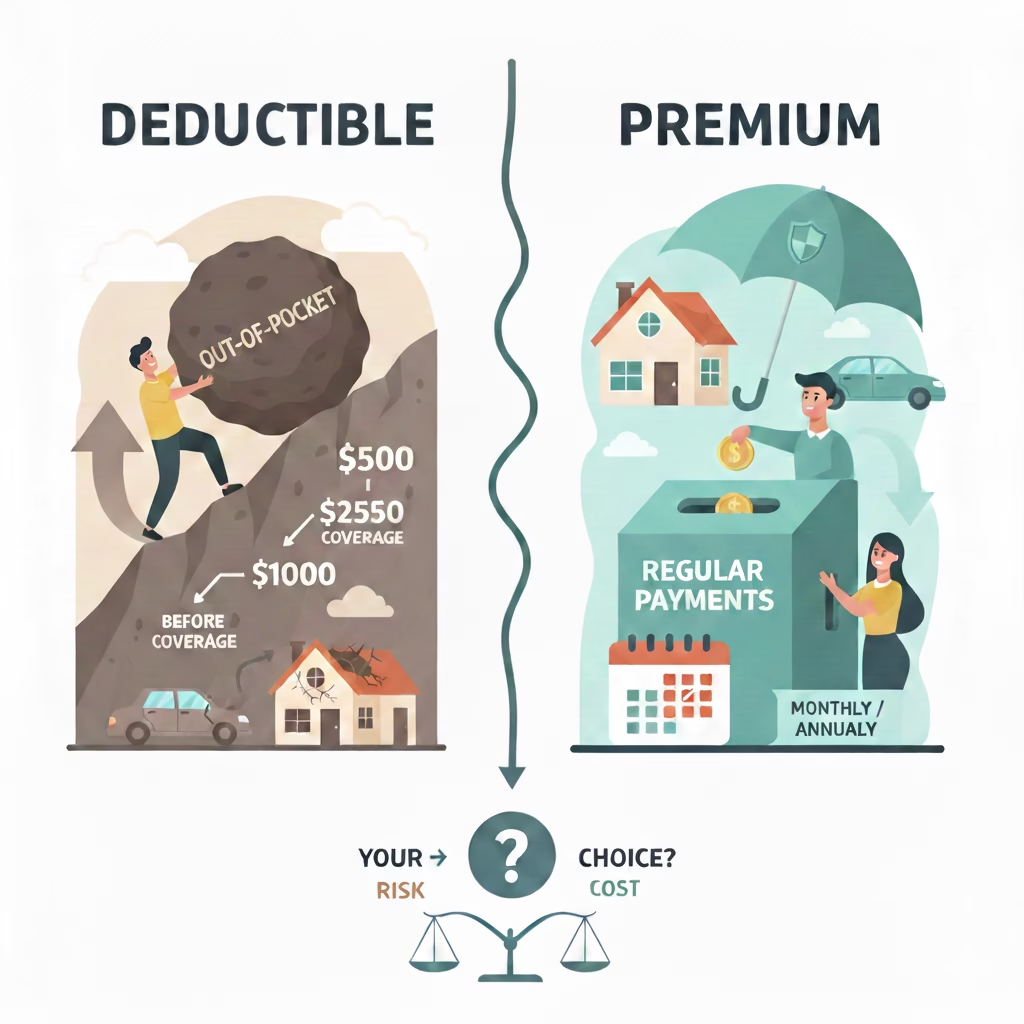
Understanding Auto Insurance Costs
Two main factors determine how much you pay for auto insurance:
1. Premium
Your premium is the amount you pay to keep your policy active. It depends on:
- Age and driving experience
- Driving history
- Location
- Vehicle type
- Coverage limits
- Claims history
2. Deductible
A deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before insurance pays a claim.
Higher deductibles:
- Lower your premium
- Increase your upfront cost during a claim
Lower deductibles:
- Raise your premium
- Reduce out-of-pocket expenses
How to Lower Your Auto Insurance Premium
You can often reduce insurance costs by:
- Maintaining a clean driving record
- Choosing a higher deductible
- Bundling auto and home or renters insurance
- Taking a defensive driving course
- Driving fewer miles
- Asking about safe driver or good student discounts
Always ask insurers about available discounts.
How to Buy Auto Insurance
Buying auto insurance doesn’t have to be complicated.
Step 1: Decide What Coverage You Need
Start with legal requirements, then add coverage based on:
- Vehicle value
- Driving habits
- Financial situation
Step 2: Gather Information
Insurers will ask about:
- Vehicle details (VIN, model, year)
- Drivers in the household
- Driving history
- Safety features
- Annual mileage
Step 3: Compare Quotes
Get quotes from multiple insurers and ensure:
- Coverage limits are identical
- Deductibles match
- Discounts are applied equally
Step 4: Review Policy Details
Look beyond price. Consider:
- Claims service reputation
- Payment plans
- Financial strength of the insurer
The Bottom Line
Auto insurance is a financial safety net that protects you, your vehicle, and others on the road. While minimum coverage may satisfy legal requirements, it may not fully protect you from major expenses.
Understanding coverage types, premiums, deductibles, and optional add-ons helps you choose a policy that fits your needs and budget. Shopping around and reviewing your policy regularly can also save you money over time.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered financial, legal, or insurance advice. Auto insurance requirements, coverage options, and regulations vary by location and individual circumstances. Always consult a licensed insurance agent, insurer, or legal professional before purchasing or changing an auto insurance policy.
People also ask:
Q1. Is auto insurance mandatory?
Yes, auto insurance is mandatory in most U.S. states and legally required in India. Minimum coverage laws vary by location.
Q2. What is the difference between collision and comprehensive insurance?
Collision covers accident-related damage, while comprehensive covers non-collision events like theft, fire, or natural disasters.
Other topics you might be interested in:
What Is Insurance? Meaning, Types, Benefits, and How It Works in the United States
10 Insurance Myths That Are Costing You More Money Than You Think
Insurance Deductible vs Premium: What’s the Difference and Which One Costs You More?