Insurance plays a crucial role in modern financial planning. From paying medical bills to rebuilding a home after a disaster, insurance helps individuals and families handle unexpected costs without destroying their finances. In the United States, where healthcare, housing, and legal expenses can be extremely high, insurance is not just helpful, it is often essential.
This guide explains what is insurance, how it works, why it matters, and how to choose the right insurance policy, all in clear, easy-to-understand language.
What Is Insurance?
Insurance is a legal contract between an individual or business (the policyholder) and an insurance company (the insurer). Under this agreement, the policyholder pays regular payments called premiums, and in return, the insurance company provides financial protection if a covered event happens.
These events may include:
- Illness or injury
- Car accidents
- Property damage
- Natural disasters
- Disability
- Death
The written contract itself is known as an insurance policy. The policy explains what is covered, what is not covered, how much the insurer will pay, and under what conditions payments are made.
In simple terms, insurance helps protect you from large financial losses when life takes an unexpected turn.
Why Is Insurance Important?
Insurance provides financial security, stability, and peace of mind. Instead of paying large costs out of pocket during emergencies, insurance allows you to share risk with an insurance company.
Key Reasons Insurance Matters
1. Financial Protection
Medical emergencies, lawsuits, or property damage can cost tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars in the U.S. Insurance helps cover these costs so your savings and income are protected.
2. Risk Management
Insurance transfers financial risk from you to the insurer. You pay smaller, predictable premiums instead of facing unpredictable, massive expenses.
3. Family Security
Life and disability insurance help protect your family’s income and lifestyle if something happens to you.
4. Access to Healthcare
Health insurance makes routine care, preventive services, and emergency treatment more affordable.
5. Legal and Lender Requirements
Auto insurance is required in nearly every U.S. state. Mortgage lenders usually require homeowners insurance before approving a loan.
Common Insurance Terms You Should Know
Understanding basic insurance terms helps you choose the right policy.
- Insurer: The insurance company providing coverage
- Policyholder: The person or business owning the policy
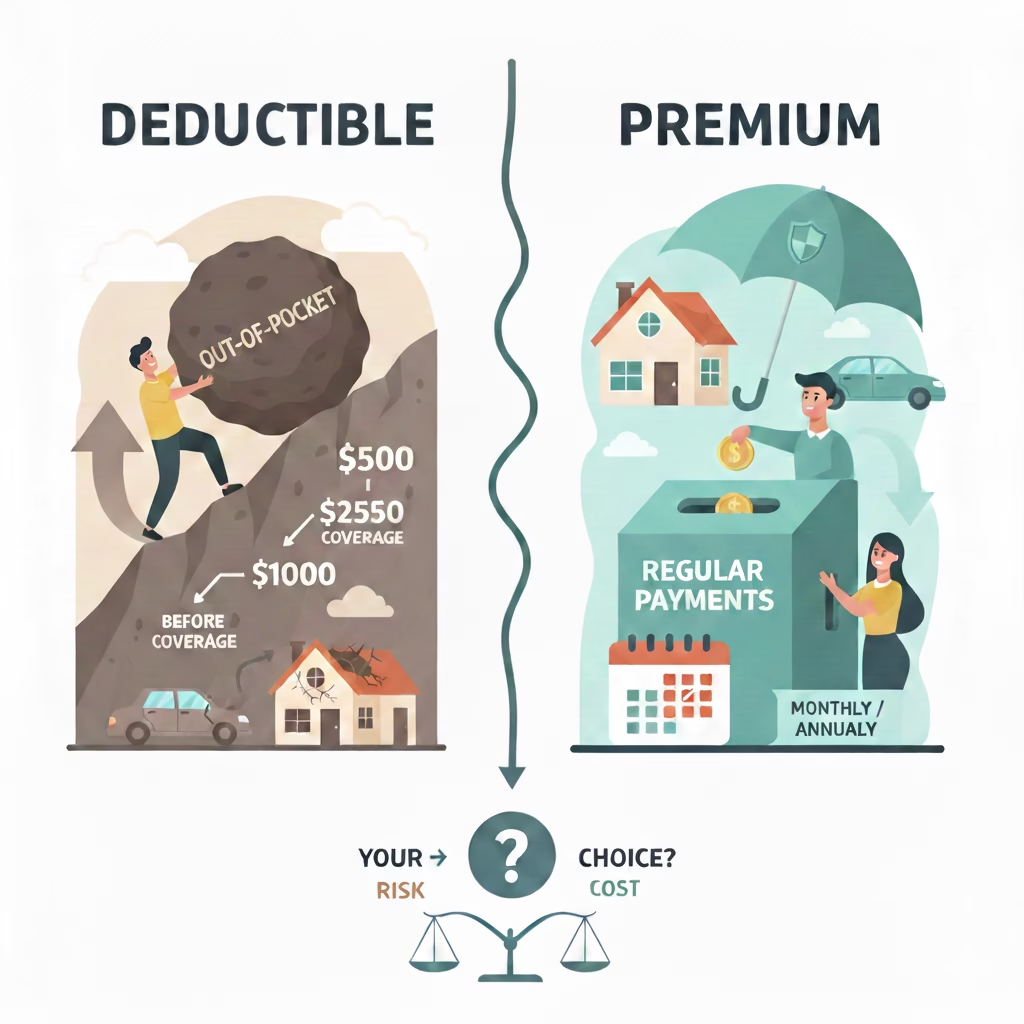
- Premium: The amount you pay to keep insurance active
- Deductible: What you pay out of pocket before insurance pays
- Policy Limit: The maximum amount the insurer will pay
- Copay: A flat fee paid for services (common in health insurance)
- Coinsurance: Your share of costs after meeting the deductible
- Claim: A request for the insurer to pay for a covered loss
How Does Insurance Work?
Insurance works by pooling risk. Many people pay premiums into a shared fund. When someone experiences a covered loss, the insurance company uses money from that pool to pay claims.
Step-by-Step Example
- You buy an insurance policy
- You pay premiums monthly or annually
- A covered event occurs (accident, illness, damage)
- You file a claim (or the provider does it for you)
- You pay your deductible (if required)
- The insurance company pays the remaining covered costs
As long as premiums are paid and the event is covered, insurance helps reduce financial strain.
Filing an Insurance Claim
A claim is a formal request asking your insurance company to pay for a covered loss.
- Claims may be filed online, by phone, or through a mobile app
- Some providers (doctors, hospitals, auto repair shops) submit claims for you
- The insurer reviews documentation and verifies coverage
- If approved, payment is issued to you or the service provider
Always keep records, receipts, and photos to support your claim.
Key Components of an Insurance Policy
Every insurance policy includes three core elements:
1. Premium
This is the cost of your insurance. Premiums vary based on factors such as age, location, health, claims history, and coverage amount.
2. Deductible
The deductible is what you pay before insurance starts paying. Higher deductibles usually mean lower premiums.
3. Policy Limit
The maximum amount the insurance company will pay for a covered loss.
Types of Insurance in the United States
There are many types of insurance available to meet different needs.
Health Insurance
Health insurance helps cover medical expenses such as:
- Doctor visits
- Hospital stays
- Prescription drugs
- Preventive care
Common Health Insurance Plans in the U.S.
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization)
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization)
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization)
- POS (Point of Service)
Health insurance can be purchased through:
- Employers
- HealthCare.gov (ACA Marketplace)
- Private insurers
- Medicare and Medicaid
Life Insurance
Life insurance pays money to your beneficiaries if you pass away.
Types of Life Insurance
Term Life Insurance
- Covers a specific period (10–30 years)
- Lower cost
- No savings component
Permanent Life Insurance
- Covers your entire life
- Builds cash value
- Higher premiums
Life insurance helps cover:
- Funeral expenses
- Mortgage payments
- Daily living costs
- Children’s education
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance helps cover costs related to car accidents and vehicle damage.
Common Coverages Include:
- Liability coverage
- Collision coverage
- Comprehensive coverage
- Personal injury protection
- Uninsured motorist coverage
Auto insurance is required by law in almost every U.S. state.
Homeowners Insurance
Home insurance protects your house and belongings.
Coverage Often Includes:
- Property damage
- Personal belongings
- Liability protection
- Temporary living expenses
Flood and earthquake insurance usually require separate policies.
Renters Insurance
Renters insurance protects personal belongings and liability for people who rent homes or apartments.
Disability Insurance
Disability insurance replaces a portion of your income if you can’t work due to illness, injury, or pregnancy.
Pet Insurance
Pet insurance helps cover veterinary bills for injuries, illnesses, and sometimes routine care.
Travel Insurance
Travel insurance covers trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage while traveling.
Benefits of Insurance
Insurance offers several key advantages:
Financial Security
Protects savings and income during emergencies.
Risk Reduction
Limits the financial impact of unexpected events.
Peace of Mind
Reduces stress by knowing help is available.
Legal Protection
Covers legal costs and liability claims.
Economic Stability
Helps individuals and businesses recover faster after losses.
What Insurance Does Not Cover
Insurance policies include exclusions. Common exclusions include:
- Intentional damage
- Fraud or criminal activity
- Normal wear and tear
- Certain high-risk activities
- Acts of war or terrorism
Always read policy documents carefully.
How to Choose the Right Insurance Plan
When selecting insurance, consider:
- Your health and age
- Dependents and family needs
- Property value
- Budget
- Risk tolerance
Compare:
- Premiums
- Deductibles
- Coverage limits
- Provider reputation
Consulting an insurance agent or employer benefits team can help.
How to Get Insurance in the U.S.
Open Enrollment
Used for health insurance through employers or the ACA Marketplace.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
Triggered by life events such as marriage, birth, or job loss.
Year-Round Enrollment
Available for auto, homeowners, life, and pet insurance.
Who Bears the Risk in Insurance?
When you buy insurance, the risk transfers from you to the insurance company. The insurer pools premiums from many policyholders to pay claims when losses occur.
The Bottom Line
Insurance is a powerful financial tool that protects individuals, families, and businesses from unexpected expenses. Whether it’s medical care, property damage, or income loss, insurance helps turn financial disasters into manageable situations.
In the United States, where costs can rise quickly, having the right insurance coverage is not optional for most people. It is a foundation of long-term financial stability and peace of mind.
People also ask:
Q1. What is insurance in simple words?
Insurance is a way to protect yourself financially by paying a small amount regularly so you don’t have to pay large costs during emergencies.
Q2. Why is insurance important in the USA?
Insurance is important because healthcare, legal, and repair costs are very high in the U.S., and insurance helps reduce financial risk.
Q3. What are the main types of insurance?
The main types are health insurance, life insurance, auto insurance, homeowners insurance, and disability insurance.
Q4. Is insurance mandatory in the United States?
Some types, such as auto insurance, are mandatory in most states, while others like health insurance depend on state laws.
Q5. How do insurance premiums work?
Premiums are regular payments you make to keep your insurance active. Higher coverage usually means higher premiums.
Other topics you might be interested in:
What Are Interest Rates and Why They Matter to the Economy?
Bond Yield Explained: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Calculate It